One Of The Best Info About Is A Star Topology LAN Or WAN

Star Topology Diagram
Decoding Network Topologies
1. Understanding Star Topology Basics
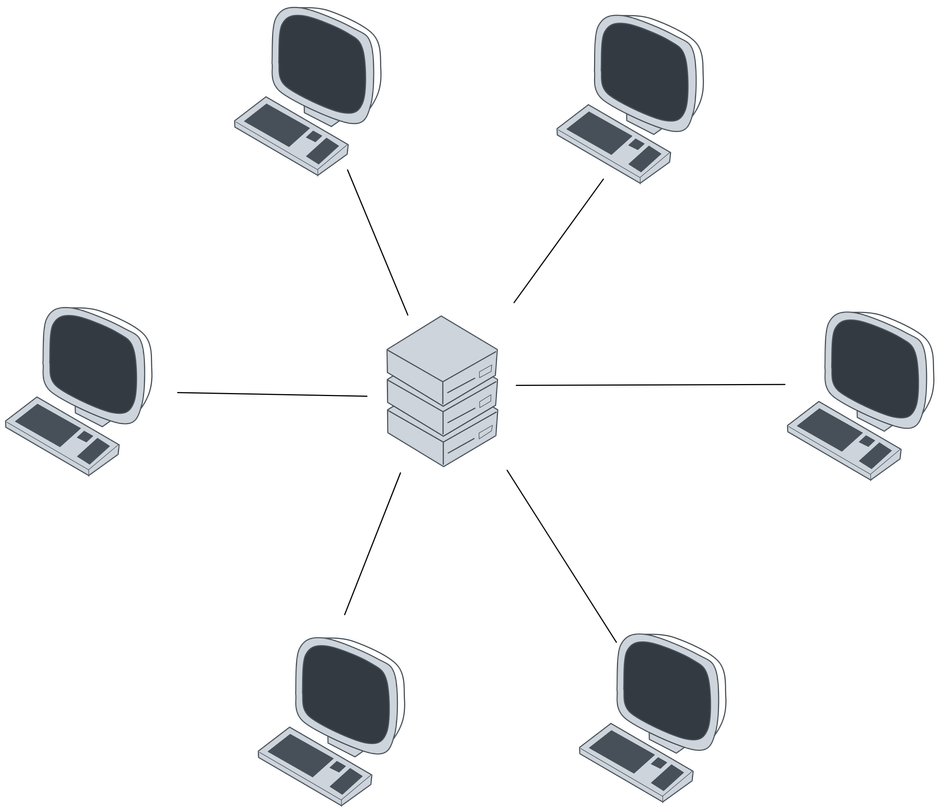
So, you're diving into the world of networks, and you've stumbled upon the term "star topology." Imagine a team huddle where everyone's looking at the coach in the center. That's essentially what a star topology is all about. All the devices in the network connect to a central hub or switch. Think of it like spokes on a wheel, all leading back to the middle. If a spoke breaks, the other spokes are fine. Same with star topology, if one device fails, the rest of the network keeps humming along, unaffected.
One of the great things about star topologies is their ease of management. Because everything runs through that central point, troubleshooting becomes a lot simpler. If there's a network problem, you often just need to check the hub or switch to figure out what's going on. Plus, adding or removing devices is a breeze. Just plug them into the hub, and you're good to go. This makes it a very popular choice for many network setups.
However, its not all sunshine and roses. The entire network's fate rests on that central hub or switch. If that central component goes down, everything goes down. Its like the team coach suddenly getting sick — the whole practice falls apart! Thats why it's vital to have reliable equipment in the center and maybe even a backup plan in case of failure.
Also, all that data traveling through the central hub can sometimes create bottlenecks. Imagine all those team members trying to talk to the coach at once. The coach can only handle so much information at a time. So, if your network experiences high traffic, you might notice some performance slowdown. Choosing the right type of central device (like a high-capacity switch) can help minimize this issue.
2. LAN or WAN
Okay, now for the big question: is a star topology a LAN or WAN? Here's the deal: a star topology is primarily associated with Local Area Networks (LANs). A LAN, as the name suggests, covers a localized area — a home, an office, a school building, that kind of thing. Star topologies thrive in these environments, providing the structured and manageable network setup that businesses and organizations need.
Think about a typical office. Each computer connects to a central switch, allowing everyone to share files, printers, and internet access within the office. That's a classic star topology in action. It provides centralized control, easy troubleshooting, and relatively fast speeds within that defined space.
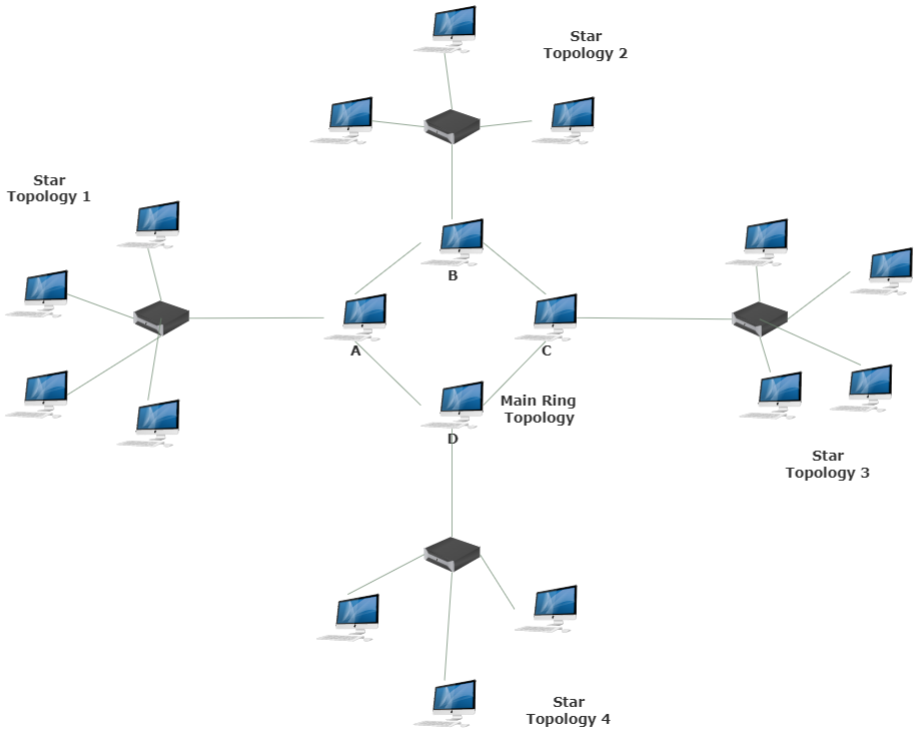
Now, could a part of a Wide Area Network (WAN) utilize star topology? Yes, absolutely. A WAN connects multiple LANs across a larger geographical area — cities, states, or even countries. While the overall WAN might use a more complex combination of topologies, individual LANs within that WAN could very well be structured as star topologies. Its like a neighborhood within a city; the city is the WAN, and the neighborhood is a LAN with star topology.
Essentially, star topologies are at home in the LAN environment because they offer a blend of manageability, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. It's the go-to setup for many localized networks. While they might play a smaller role in the grand scheme of a WAN, their contribution at the LAN level is significant.

A Guide To Star Topology. Definition, Practices, And Importance
Delving Deeper
3. Central Hub vs. Switch
At the core of any star topology sits the central hub or switch, the maestro conducting the network symphony. While both achieve the same fundamental goal — connecting devices — they operate in fundamentally different ways. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for maximizing your network's efficiency.
A hub acts as a simple repeater. When it receives a signal from one device, it blasts that signal out to every other device connected to it. Think of it like shouting something in a crowded room; everyone hears it, but only the intended recipient pays attention. This can lead to collisions and inefficiencies, especially in networks with heavy traffic. It's kind of like everyone shouting at once; nobody understands anything.
A switch, on the other hand, is much smarter. It learns the MAC addresses of all the devices connected to it and can then direct traffic only to the intended recipient. It's like whispering directly to the person you want to talk to. This dramatically reduces collisions and improves network performance. Its the reason switches are so prevalent in modern network setups.
Therefore, although the topology might be a star, the use of a switch rather than a hub greatly affects network speed and performance. When setting up a network, it's generally recommended to use a switch for optimal performance, especially for networks dealing with video streaming, large file transfers, or gaming.
4. Cable Considerations
The cables linking each device to the central hub or switch are the veins of your network, carrying data back and forth. The type of cable you choose can significantly impact your network's speed and reliability. Let's explore some common options.
Twisted pair cables, such as Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a, are commonly used in star topologies. These cables consist of pairs of wires twisted together to reduce interference and improve signal quality. Cat5e is suitable for speeds up to 1 Gigabit Ethernet, while Cat6 and Cat6a can handle speeds up to 10 Gigabit Ethernet and beyond, depending on cable length and installation quality.
Fiber optic cables offer even higher speeds and greater bandwidth, making them ideal for demanding applications or longer distances. Fiber uses light to transmit data, which is resistant to electromagnetic interference and can travel much further without signal degradation compared to copper cables. However, fiber optic cables are typically more expensive and require specialized equipment for installation.
Wireless connections, while technically not a "cable," can also be part of a star topology. The central hub is typically a Wireless Access Point that all the devices connect to wirelessly. The advantage here is mobility, but the potential downsides are speed fluctuations, increased latency, and potential security vulnerabilities. So if you value speed and reliability, wired connections are generally preferred for the devices that need it most.
A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Star Topology In Computer Networks
Practical Applications and Benefits
5. Star Topologies in Small Businesses
Small businesses often find star topologies to be the perfect fit for their networking needs. They offer a blend of simplicity, scalability, and cost-effectiveness that makes them ideal for smaller environments. Here's how they play out in practice.
Imagine a small accounting firm with about ten employees. Each employee needs to access shared files, printers, and the internet. A star topology, with a central switch and each computer connected to that switch, provides a reliable and easily manageable solution. The owner can easily add new computers or troubleshoot network issues from a central location.
Furthermore, star topologies allow for centralized security measures. A firewall and other security appliances can be installed at the central switch, protecting the entire network from external threats. It's like having a security guard at the front door, keeping everyone inside safe and secure.
Another benefit for small businesses is the ability to prioritize network traffic. Quality of Service (QoS) settings can be configured on the switch to ensure that critical applications, such as voice over IP (VoIP) phones, receive priority over less important traffic. This ensures clear and reliable communication for the business.
6. Star Topologies in Home Networks
Star topologies aren't just for businesses; they're also a popular choice for home networks. They provide a structured and reliable way to connect multiple devices, such as computers, smartphones, smart TVs, and gaming consoles.
Most home networks use a router as their central hub. The router combines the functions of a switch, a firewall, and a wireless access point, providing a single point of connection for all your devices. Each device connects to the router either via Ethernet cable or wirelessly.
The star topology allows for easy sharing of resources within the home network. You can easily share files between computers, stream media to your smart TV, or print documents from any device. It's like having a digital hub for all your entertainment and productivity needs.
Furthermore, star topologies offer a degree of isolation between devices. If one device on the network is infected with malware, it's less likely to spread to other devices compared to some other network topologies. While not foolproof, this added layer of security can help protect your home network from threats.
A Quick Guide To Star Topology Diagram (With Templates)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
7. Q
A: Star topologies offer several key advantages. They are relatively easy to install and manage, offer centralized control and troubleshooting, and provide good scalability. Plus, the failure of one device doesn't typically affect the rest of the network.
8. Q
A: The main disadvantage is the reliance on the central hub or switch. If that central component fails, the entire network goes down. Also, high traffic on the network can create bottlenecks, impacting performance. The central device needs to be robust enough to handle the workload.
9. Q
A: While the overall WAN architecture is usually more complex, individual LANs within a WAN can certainly use a star topology. It's like having multiple office buildings (LANs with star topology) connected to form a larger corporate network (WAN).

Star Ring Topology